Bell uh-1y venom
Содержание:
Specifications[edit]
UH-1Y firing rockets
Data from Bell UH-1Y guide, International Directory of Civil Aircraft
General characteristics
- Crew: one or two pilots, plus crew chief, other crew members as mission requires
- Capacity: 6,660 lb (3,020 kg) including up to ten crashworthy passenger seats, six litters or equivalent cargo
- Length: 58 ft 4 in (17.78 m)
- Rotor diameter: 48 ft 10 in (14.88 m)
- Height: 14 ft 7 in (4.5 m)
- Disc area: 1,808 ft² (168.0 m²)
- Empty weight: 11,840 lb (5,370 kg)
- Useful load: 6,660 lb (3,020 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 18,500 lb (8,390 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × General Electric T700-GE-401C turboshaft, 1,828 shp for 2.5 min; 1,546 shp continuous (1,360 kW for 2.5 min; 1,150 kW continuous) each
Performance
- 164 kn (189 mph, 304 km/h) for 30 minutes
- 158 kn, 182 mph, 293 km/h (long range cruise (LRC): 135 kn, 155 mph, 250 km/h)
- 198 knots (227 mph, 366 km/h)
- Combat radius: 130 nmi (150 mi, 241 km) with 2,182 lb, 990 kg payload
- Endurance: 3.3 hr
- Service ceiling: 20,000+ ft (6,100+ m)
- Rate of climb: 2,520 ft/min (12.8 m/s)
Armament
- 2 external stations for 70 mm (2.75 in) Hydra 70 or APKWS II rockets
- 2 pintle mounts for 7.62×51 mm machine guns, .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, or 7.62×51 mm NATO GAU-17/A Gatling guns
Создание вертолета.
В начале 60-х ряд авиационных фирм США начали разработку боевого винтокрыла. Наиболее впечатлил военных YAH-56 «Шайен» фирмы «Локхид», но из-за дороговизны и сложности конструкции его серийное производство отложили на неопределенное время. Шла война во Вьетнаме, американское командование решило не тянуть время и в декабре 1964 г. поручило фирме «Белл» разработать ударный вертолет в кратчайшие сроки. Заказ был выполнен и в сентябре этого же года начались летные испытания UH-1H, вертолет был принят на вооружение под обозначением AH-1G «Хью Кобра».
Составляющие вертолета.
При разработке вертолета конструкторы пошли кратчайшим путем: «Кобра» является глубокой модернизацией UH-1 в сочетании с некоторыми особенностями конструкции опытного вертолета Модель 207 «Сиукс Скаут». Расположение двигателя, хвостовую балку, трансмиссию и несущий винт (с небольшими изменениями) полностью позаимствованы у UH-1. В тоже время фюзеляж стал значительно уже, что способствовало увеличению скорости.
Значительным изменениям подверглась его передняя часть. Кабины пилота (сзади) и стрелка (впереди) были расположены тандемом. Конструкция фонаря обеспечивала хороший обзор. После некоторых сомнений на вертолете решили оставить лыжное шасси, поскольку благодаря конструкции фюзеляжа он так обладал требуемой скоростью. Удачным было расположение вооружения. Шестиствольный M134 «Миниган» размещался в турели под кабиной, а по бокам фюзеляжа имелись четыре пилона, на которых можно было устанавливать дополнительные пулеметы, 20-мм пушки, гранатометы, НАР и ПТУРы.
Шестиствольный M134 «Миниган».
Боевое применение.
В августе 1967 г. первые «Кобры» были доставлены во Вьетнам. Их боевое применение началось с октября и оказалось очень результативным. Настоящее признание в американских войсках они получили во время наступления вьетконговцев в январе 1968 г. Основными задачами этих вертолетов было уничтожение живой силы противника, боевых катеров, ДОТов и легкой техники.
Варианты окраски
«Кобры» также занимались сопровождением десантных UH-1. Обладая большей огневой мощью, они уничтожали средства ПВО в случае их обнаружения. Столкнувшись с тяжелой бронетехникой советского производства, американские пилоты ощутили недостаточную эффективность НАР и авиационных пушек. Для исправления ситуации вертолеты оснастили ПТУР «Тоу».
Неприятным сюрпризом со стороны вьетконговцев стали советские ПЗРК «Стрела». Среди «Кобр», отличавшихся хорошей живучестью, появились потери. Для устранения данной угрозы конструкторы изменили конструкцию системы отвода горячих газов. Теперь коленчатая труба отводила их вверх, в строну несущего винта, где сильный поток воздуха моментально рассеивал их.
Советские ПЗРК «Стрела».
Характеристики.
Максимальный взлетный вес 4536 кг. Максимальная скорость 315 км/ч. Максимальная скороподъемность 8,22 м/с. Статический потолок 3720 м.
Полные характеристики
Armament
The pilot controls the Hydra 70 rocket pods while the crew chief gunners handle the M134 miniguns.
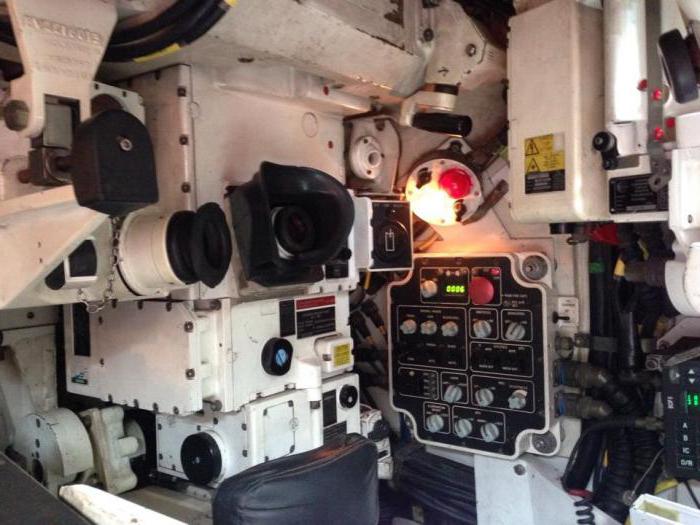
The co-pilot/observer seat has access to a targeting pod with a laser designator. For optics, they alone can switch between three fields of view and toggle between regular day, night or green/black-hot thermal vision modes:
Hydra 70
| Damage type | Base damage value | Maximum speed (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| High-Explosive | 150 | 740 |
Forward-facing, twin 70 mm rocket pods. Fires unguided rockets that are strong against clumped-up infantry and unarmoured/lightly-armoured ground vehicles.
Rockets are always launched in pairs. There is an imposed delay of 0.08 seconds in-between launches (750 rounds per minute). They have initial velocities of 44 m/s and take a further 1.1 seconds for their motors to reach a top speed of 740 m/s in mid-flight. The warheads themselves have a blast radius of 12 metres.
M134
| Base damage value | Aerodynamic friction | Initial velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | -0.0009324 | 900 |
Side door 7.62 mm Gatling guns. Useful for suppressing infantry and disabling unarmoured ground vehicles.
It has a variable fire rate depending on the selected fire mode:
- LOW: ~ 666 RPM
- HIGH: 1,200 RPM
Muzzle velocity is set to 900 m/s for both M134s. Accuracy-wise, they have fixed dispersion values of 0.0017 rad against targets at distances of up to 800 metres away.
Rotation limits depend on where the guns are mounted but horizontally are always restricted to 185 degrees in both directions. Vertically however, this is limited to an elevation of 30 degrees and depression of 60 degrees only.
Development[edit]
Over the years, new avionics and radios, modern door guns, and safety upgrades have greatly increased the UH-1N’s empty weight. With a maximum speed around 100 knots (190 km/h) and an inability to lift much more than its own crew, fuel, and ammunition, the UH-1N had limited capabilities as a transport.[citation needed]
In 1996, the United States Marine Corps launched the H-1 upgrade program. A contract was signed with Bell Helicopter for upgrading 100 UH-1Ns into UH-1Ys and upgrading 180 AH-1Ws into AH-1Zs. The H-1 program created completely modernized attack and utility helicopters with considerable design commonality to reduce operating costs. The UH-1Y and AH-1Z share a common tailboom, engines, rotor system, drivetrain, avionics architecture, software, controls, and displays for over 84% identical components.
A UH-1Y during sea trials aboard USS Bataan
The Y-model upgrades pilot avionics to a glass cockpit, adds further safety modifications, and provides the UH-1 with a modern FLIR system. However, the biggest improvement is an increase in engine power. By replacing the engines and the two-bladed rotor system with four composite blades, the Y-model returns the Huey to the utility role for which it was designed. Originally, the UH-1Y was to have been remanufactured from UH-1N airframes, but in April 2005, approval was granted to build them as new helicopters.
The Y-model updates an airframe that has been central to Marine Corps aviation in Iraq.[citation needed] The Huey has many mission requirements, including command and control (C2), escort, reconnaissance, troop transport, medical evacuation, and close air support. Typically, detachments of two to four Hueys have been deployed with detachments of four to eight Cobras.[citation needed] The forward-mounted weaponry of the Cobra combined with the door guns of the Huey provides a 240° field of fire.[citation needed]
Bell delivered two UH-1Ys to the U.S. Marine Corps in February 2008 and full-rate production was begun in September 2009. The Marine Corps plans to buy 160 Y-models to replace their inventory of N-models.
Design
The UH-1Y is an armed, four-bladed, twin-engined rotary-wing helicopter.
It is a modern iteration of the venerable UH-1 helicopter, and combines the versatility and reliability of the original UH-1 airframe with modern avionics and a new propulsion system.
Armament
It is armed with twin forward-facing 70 mm rocket pods, with each pod loaded with 7 high-explosive dual purpose (HEDP) rockets for a total of 14 rockets.
It also has two more 7.62 mm miniguns with one fitted to each side of the passenger cabin. Both miniguns are fed by linked 2,000-round belts, with a combined total of 4,000 rounds.
Features
Designed to ferry Marines into combat as well as provide fire support as a light gunship, the UH-1Y is a highly versatile transport helicopter.
The co-pilot/observer also has access to a laser designator (using the nose-mounted targeting pod) that can be used to guide precision bombs like the GBU-12 from other aircraft, allowing the UH-1Y to act in a forward air control role as well.
Marines dismount from a UH-1Y.
While it cannot carry as many troops as the larger MH-60S, it has a more compact and nimbler airframe that lets it land in areas with minimal clearance.
Drawbacks
The UH-1Y’s small size does come at the cost of armour however, as the UH-1Y is significantly more vulnerable to ground fire than the MH-60S as a result of being smaller and lighter.
Crew Capacity
The UH-1Y has a seating capacity of eleven personnel (including the crew). This consists of both the pilot and co-pilot who doubles as an observer, and up to seven passengers who sit in the rear cabin facing towards the port and starboard sides of the fuselage (the passengers in the centre of the cabin sit facing either forward or towards the back instead).
Operational history[edit]
The UH-1Y and AH-1Z completed their developmental testing in early 2006. During the first quarter of 2006 the UH-1Ys were transferred to the Operational Test Unit at NAS Patuxent River, where they began operational evaluation testing. In February 2008, the UH-1Y and AH-1Z began the second and final portion of testing.
On 8 August 2008, the Marine Corps certified the UH-1Y as operationally capable and it was deployed for the first time in January 2009 as part of the aviation combat element of the 13th Marine Expeditionary Unit. The UH-1N Twin Huey was retired by the Marines in August 2014, making the UH-1Y the Marine Corps’ standard utility helicopter.
Potential operatorsedit
On 11 October 2017, the Defense Security Cooperation Agency notified the United States Congress of the potential sale of 12 UH-1Ys and related systems and support to the Czech Republic for a cost of US$575 million. In December 2019, an order for eight UH-1Y helicopters was approved.
See also
Aircraft of comparable role and configuration
- MH-60S (Alternate USMC counterpart)
- AH-11 Wildcat (British Army counterpart, ArmA 2: BAF only)
- WY-55 Hellcat (AAF counterpart, ArmA 3 only)
| Vehicles of ArmA 2 | |
|---|---|
| Wheeled | 9P117 SCUD-B • ATV • BRDM-2* • BTR-40 • BTR-60 • BTR-90 • BM-21 Grad* • Bus • Car • Dingo 2 CZ • Hatchback • HMMWV* • GAZ • Jackal 2 MWMIK • Kamaz • Lada* • LAV-25 • Military Offroad • Motorcycle* (Old moto) • Mountain bike (Old bike) • MTVR* • Offroad* • Pandur II 8×8 CZ • Pickup* • RM-70 • S1203 • Sedan • Stryker (MGS) • SUV (Armored SUV) • T810 • Tractor • Touring Car • Towing Tractor • UAZ-469* • Ural* • V3S* • Vodnik |
| Tracked | 2S6M Tunguska • AAVP-7A1 • BMP-2 • BMP-3 • BVP-1 • FV510 Warrior • M1 Abrams* (M1A2 TUSK*) • M113 • M2 Bradley • M270 MLRS* • T-34* • T-55 • T-72* (T-72M4 CZ) • T-90 • ZSU-23-4* |
| Rotor-wing | AH-1Z • AH-6J Little Bird () • AH-11 Wildcat • AH-64D* (AH-1) • CH-47F Chinook () • Ka-52 • Ka-60 • Ka-137 • Merlin HC3 • MH-6J Little Bird • Mi-8MTV-3* (Mi-17*) • Mi-24P (*, *) • UH-1Y (UH-1H) • UH-60 Black Hawk (MH-60S) |
| Fixed-wing | A-10 Thunderbolt II* • An-2 • AV-8B Harrier • C-130J Hercules* • F-35 Lightning II • L-159 ALCA • L-39ZA (L-39C) • MQ-9 Reaper* • MV-22 Osprey • Pchela-1T • Su-39 (Su-25*) • Su-34 |
| Aquatic | CRRC • Fishing Boat • PBX • RHIB • Small Boat |
| (Parenthesis) denote variants.* indicates partial DLC dependency.Operation Arrowhead | British Armed Forces | Private Military Company | Army of the Czech Republic |
| USMC — Vehicles (ArmA 2) | |
|---|---|
| Wheeled | HMMWV • LAV-25 • Motorcycle • Mountain bike • MTVR • Towing Tractor |
| Tracked | AAVP-7A1 • M1 Abrams (M1A2 TUSK) • M270 MLRS |
| Rotor-wing | AH-1Z • AH-64D • UH-1Y • MH-60S |
| Fixed-wing | A-10 Thunderbolt II • AV-8B Harrier • C-130J Hercules • F-35 Lightning II • MQ-9 Reaper • MV-22 Osprey |
| Aquatic | CRRC • RHIB |
| (Parenthesis) denote variants. |
Design[edit]
UH-1Y refueling at night
The UH-1Y variant modernizes the UH-1 design. Its most noticeable upgrade over previous variants is a four-blade, all-composite rotor system designed to withstand up to 23 mm rounds. A 21-inch (530 mm) fuselage extension just forward of the main door has been added for more capacity. The UH-1Y features upgraded engines and transmissions, a digital cockpit with flat-panel multifunctional displays, and an 84% parts commonality with the AH-1Z. Compared to the UH-1N, the Y-model has an increased payload, almost 50% greater range, a reduction in vibration, and higher cruising speed.
Trivia
- Just like the MV-22, the UH-1Y was not initially «upgraded» to use countermeasure flares with the release of the Operation Arrowhead expansion pack
Following the release of the Community Configuration Project updates for the Steam version, the UH-1Y’s pilot was granted access to defensive countermeasures (while the co-pilot’s targeting pod was given thermal vision capabilities). However, this update is not available to non-Steam versions of the game without manually applying the patch itself.
(in contrast to its real-world counterpart).
- The UH-1Y has a cinematic-only version that is hidden in the game and cannot be spawned or placed in the editor without the use of scripting commands.
- This UH-1Y (Classname: UH1Y_cutscene) can only be seen officially in the opening cutscene for the First to Fight mission in the Operation Harvest Red campaign. The main difference with this variant is that the seats have been re-arranged so that the passengers sit facing forward towards one specific seat. This was done to ensure that the Razor Team members could clearly see Miles giving the briefing.
- In addition, there is also a crashed version of the UH-1Y that can be freely placed in the editor or spawned via script. It cannot be flown for obvious reasons, but still features a usable minigun that can be manned by a gunner (it is treated as a static turret).
- Despite its Armoury Description stating that it is armed with dual «M240D
No USMC-operated UH-1Ys are available with side-mounted M240s, though Takistani Army-operated UH-1Hs that were later added with the Operation Arrowhead expansion pack are oddly enough, fitted with the M240 (it should be noted that regular Takistani Army infantry units do not utilise the M240).
» machine guns, the actual in-game UH-1Y is armed with twin M134 miniguns instead.
Protection
The UH-1Y has a base armour value of 30.
Engine
The engine will be disabled if it takes more than 7.5 points of damage. A damaged engine will provide greatly reduced power output, preventing the UH-1Y from being able to attain its top speed.
Main rotor
The main rotor can only withstand 9 points of damage. Disabling the main rotor will prevent the pilot from being able to maintain lift. 30% of damage is always transferred onto the main «health» pool of the UH-1Y.
Tail rotor
The tail rotor is limited to taking just 6 points of damage. Disabling the tail rotor will prevent the pilot from being able to control the main rotor’s torque. At least 10% of damage will be shared with the main «health» pool of the UH-1Y.
Вьетнамская война
Из-за широкого спектра своих функциональных возможностей «Хьюи» стал символом Вьетнамской войны. За все время конфликта вертолет UH-1 налетал 9 713 762 часа.
Во Вьетнамской войне были использованы три основные конфигурации «Хьюи»:
- Slick: перевозка войск или грузов. Вооружение: M60 на каждой стороне фюзеляжа;
- Gunship: наземная поддержка или сопровождение. Вооружение (в зависимости от времени, задач и версий): два пулемета 7,62х51 мм, соединенные параллельно на каждой стороне фюзеляжа; гранатомет, установленный под носовой частью самолета, и две 70-мм тройных ракетных установки;
- Medevac: санитарная эвакуация.

Первая воздушная победа вертолета произошла 12 января 1968 года, когда экипаж UH-1D обстрелял два самолета Ан-2 принадлежащих вьетнамским народным ВВС. Самолеты были уничтожены.
Модификации
Bell 204:
- UH-1A — первая серийная версия с двигателем Lycoming T53 L-1. Первоначально вертолет назывался HU-1A, отсюда и неофициальное прозвище Huey;
- TH-1A — тренажерная модификация;
- XH-1A — тестовая модификация, оснащенная гранатометом;
- UH-1B — версия с турбиной T53-L-5 960 WPS. Ротор был увеличен до 13 м в диаметре, а лопасти ротора до 53 см в ширину. Кабина увеличена до семи человек;
- UH-1C — версия с турбиной мощностью в 820 кВт (1100 Вт/с) T53-L-9 или L-11, лопастями Bell 540 шириной 69 см, а также с удлиненным хвостом для лечшей маневренности. Увеличен объем топливного бака, и введен дополнительный гидравлический двойной контроль (для повышения устойчивости к пулям);
- UH-1M — оснащен турбиной Lycoming T53 L-13 мощностью 1000 кВт (1400 л.с.);
- UH-1E — военно-морской вариант UH-1B/C, изготовленный из алюминия (для защиты от коррозии). Многие данные модификации позже получили турбину Lycoming T53 L-13 мощностью 1000 кВт (1400 л.с.).
Bell 205:
- YUH-1D — прототип с расширенной вместимостью для 13 пассажиров или 6 носилок. Прототип был оснащен турбиной T53 L-9 и впервые взлетел в августе 1960 года;
- UH-1D — производственная версия YUH-1D с двигателем Lycoming T53 L-11;
- HH-1D — переоборудованный UH-1D с резервуаром для пожаротушения объемом в 190 л;
- EH-1H — модификация для радиоэлектронной борьбы;
- HH-1 Н — модификация, предназначенная для пожаротушения;
- HH-1K — SAR версия UH-1E для ВМС США с обновленной авионикой и турбиной Lycoming T53 L-13;
- UH-1L — версия UH-1C для ВМС США с турбиной Lycoming T53 L-13;
- JUH-1 SOTAS модификация, оснащенная радаром AN/APS-94;
- TH-1L — тренажерная версия UH-1L для Военно-морского флота;
- VH-1N — модификация VIP класса для перевозки высокопоставленных чиновников;
- UH-1P — бронированный UH-1F для ВВС США, предназначенный для психологической войны во Вьетнаме.
Bell 212:
UH-1N «Твин Хьюи» – основан на двухмоторном Bell 212. Оснащен двумя турбированными турбокомпрессорами Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6T-3/T400 1342 кВт (1800 Вт/с).
Bell 412:
UH-1Y «Веном» — также называемый Super Huey. Модернизированная версия UH-1N на базе Bell 412 с усовершенствованной авионикой, технологией «Стеклянная кабина», двумя турбинами General Electric T700 GE 401C мощностью 1150 кВт (1546 WPS) и четырехлопастным ротором.